If you’ve been eating less, trying to be active, and still can’t lose stubborn belly fat, the problem is probably not calories.
It’s your blood sugar. In reality, it comes from hormones—especially insulin, which is controlled by your blood sugar
When blood sugar constantly spikes and crashes, your body switches into fat-storage mode—especially around the belly. This is one of the most overlooked reasons people stay stuck with midsection fat no matter how “healthy” they try to be.
Let’s break it down. This is not theory. It is biology.
What Blood Sugar Really Does in Your Body
Blood sugar (glucose) is the fuel your body uses for energy.
When you eat carbohydrates or sugar, glucose enters your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose into your cells.
When blood sugar is stable:
- Your cells get steady energy
- Fat burning stays active
- Hunger stays controlled
But when blood sugar spikes too high and crashes too low, your body enters fat-storage mode.
How Blood Sugar Controls Fat Storage
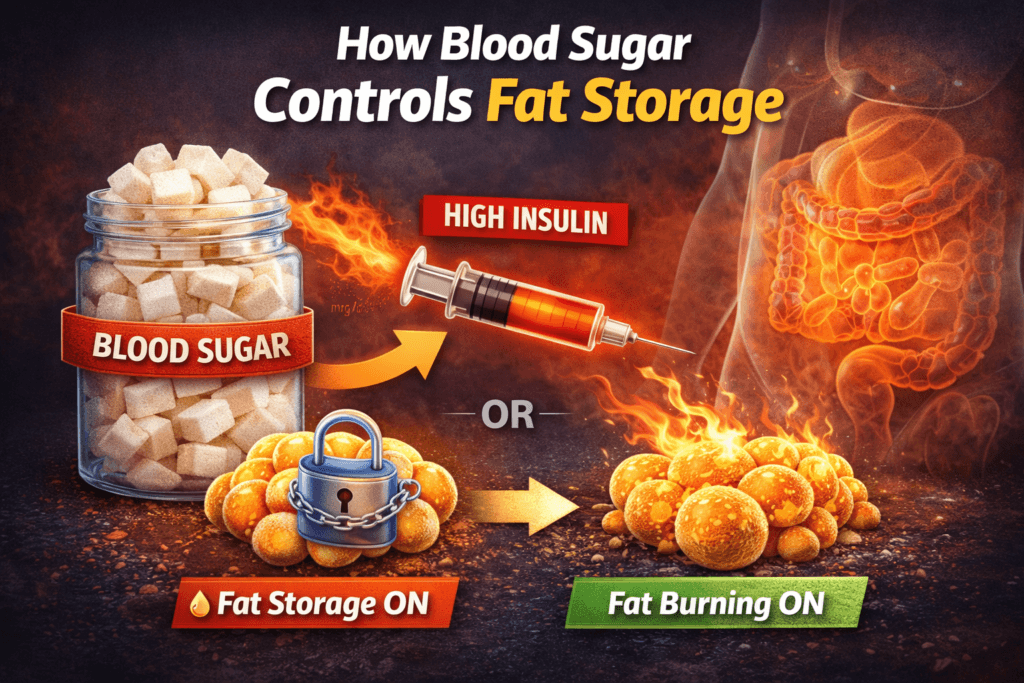
Whenever you eat carbohydrates or sugar, glucose enters your bloodstream.
Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that pushes glucose into your cells.
But insulin also does something else:
It blocks fat burning and turns fat storage on.
A landmark review in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that high insulin levels prevent fat cells from releasing stored fat and promote the accumulation of abdominal fat (AJCN, 2015).
That means:
- High insulin → fat storage
- Low insulin → fat burning
Blood sugar spikes = insulin spikes = belly fat.
Why Blood Sugar Spikes Create Belly Fat
Every time blood sugar rises sharply, insulin is released.
And insulin has one main job:
👉 Store energy
That energy is stored as
- Fat in fat cells
- Sugar in the liver and muscles
High insulin = fat storage ON
Low insulin = fat burning ON
Studies show that frequent insulin spikes increase fat storage and make fat harder to release, especially visceral belly fat (the dangerous fat around your organs) (Harvard Medical School, 2020).
When insulin is constantly high:
- Your body can’t access stored fat
- Your metabolism slows
- Belly fat becomes stubborn
Why Blood Sugar Spikes Target the Belly
Belly fat (visceral fat) has more insulin receptors than other fat cells.
This makes it especially sensitive to insulin.
A study in the Diabetes journal showed that people with insulin resistance store significantly more fat in the abdominal region than elsewhere (Diabetes, 2014).
So when blood sugar rises repeatedly:
- Fat is preferentially stored around the waist
- Belly fat becomes stubborn and hard to lose
Blood Sugar Crashes Make You Tired and Hungry

After a blood sugar spike comes a crash.
When glucose drops too low, your body releases:
- Cortisol (stress hormone)
- Adrenaline
These hormones:
- Increase cravings
- Trigger hunger
- Signal the body to store fat
This is why people feel:
- Tired
- Shaky
- Irritable
- Desperate for sugar
And when cortisol stays high, belly fat increases even more.
Why Belly Fat Is the First Place Blood Sugar Stores Energy
The belly area has more insulin receptors than other fat cells.
That means:
- When insulin is high
- More fat is stored in the belly
That’s why unstable blood sugar almost always shows up as:
- Lower belly fat
- Love handles
- Bloating
It’s not random—it’s biological.
Read: Why Belly Fat Is So Stubborn.
Blood Sugar Crashes Trigger Cortisol and Cravings
After a spike comes a crash.
When blood glucose drops, your body releases:
- Cortisol (stress hormone)
- Epinephrine
A study in Endocrine Reviews found that low blood glucose directly increases cortisol levels, pushing the body into survival mode (Endocrine Reviews, 2016).
Cortisol:
- Increases cravings
- Promotes fat storage
- Specifically targets belly fat
Read: Why Body Stores Fat. When You’re Tired
Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Blocking Fat Loss
You may be dealing with this if you:
- Feel tired after meals
- Crave sugar or bread
- Get hungry quickly
- Wake up tired
- Gain weight around the waist
These are signs of insulin resistance—when your cells stop responding properly to insulin, forcing your body to produce more of it.
And more insulin means more belly fat.
Why Blood Sugar Instability Slows Your Metabolism
Unstable blood sugar makes your cells resistant to insulin.
This condition—insulin resistance—forces the body to produce more insulin, which locks fat inside fat cells.
Harvard Medical School reports that insulin resistance is one of the strongest predictors of belly fat and metabolic slowdown (Harvard Health Publishing, 2021).
Your body isn’t refusing to burn fat.
It is being hormonally blocked from doing so.
Read: Slow Metabolism And Fat Storage
How to Stabilize Blood Sugar and Unlock Fat Burning

This is where everything changes.
You don’t need extreme dieting.
You need blood sugar control.
1. Eat Protein First
Protein slows glucose absorption and reduces insulin spikes.
Studies show protein improves insulin sensitivity and increases fat burning (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition).
Read: How Smoothie Stabilize Your blood Sugar
2. Avoid Sugar and Refined Carbs Early
Sugar and white bread cause the biggest glucose spikes.
Avoiding them in the morning helps keep insulin low all day.
2.1 Refined carbs create the largest insulin spikes.
A clinical trial in Nutrients found that low-glycemic diets significantly reduced insulin and belly fat (Nutrients, 2020).
3. Walk After Meals
Just 10–15 minutes of walking lowers blood sugar by helping muscles absorb glucose without insulin.
3.1 Walking helps muscles absorb glucose without insulin.
A study in Diabetes Care found that 10 minutes of walking after meals lowered blood sugar by up to 22% (Diabetes Care, 2016).
4. Drink Enough Water
Dehydration increases blood sugar and cortisol.
5. Get Sunlight and Sleep
Poor sleep raises insulin resistance and belly fat.
Sunlight regulates circadian rhythm and blood sugar control.
5.1 Poor sleep increases insulin resistance and cortisol.
A study in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that even one night of sleep deprivation reduces insulin sensitivity by 25% (JCEM, 2015).
Why This Connects to Energy and Hormones
Blood sugar instability:
- Increases cortisol
- Reduces energy
- Slows metabolism
- Blocks fat burning
This is why you feel tired and stuck.
It connects directly to:
- Energy metabolism
- Stress hormones
- Fat storage
We’re not fixing weight loss —
We’re fixing the system that controls weight loss.
Why This Explains Stubborn Belly Fat
If your blood sugar is unstable:
- Insulin stays high
- Cortisol stays elevated
- Fat burning stays OFF
That’s why dieting alone doesn’t work.
You must fix blood sugar, energy, and hormones first.
FAQ
Does blood sugar really cause belly fat?
Yes. Elevated insulin caused by blood sugar spikes directly increases fat storage, especially around the waist.
Can I lose belly fat without fixing blood sugar?
It’s very difficult. Your body will stay in storage mode.
Do smoothies help blood sugar?
When made correctly (with protein, fiber, and healthy fats), smoothies stabilize blood sugar instead of spiking it.
Is this why diets fail?
Yes. Most diets ignore hormones and blood sugar.
Final Thought
If your belly fat won’t go away, your body is not broken—it’s responding to unstable blood sugar.
Fix that, and fat burning turns back on.
👉 If you have a question about blood sugar, cravings, or belly fat, leave it in the comments. I read and reply to every one.
