
Intro
If you’re eating “healthy,” moving regularly, and still struggling with stubborn belly fat—and especially if you feel tired, drained, or “wired-but-tired”—your metabolism isn’t the problem.
The real issue is often low energy due to metabolic resistance, which shuts down your fat-burning systems and forces your body into fat storage mode.
This article explains, in science-backed language, how energy production, hormones, and metabolic regulation intersect—and how to break out of the fatigue-fat trap naturally.
If energy and metabolism are a mystery to you right now…
You’re about to understand the science behind it.
Let’s dive in.
🔬 What Is Metabolism?
Metabolism isn’t just “how fast you burn calories.” It is the sum of all chemical reactions in your body that turn food into:
- Energy
- Heat
- Fuel for every cell
Your metabolism determines whether your body burns fat for energy or stores it.
Two systems govern this:
| System | Function |
|---|---|
| Catabolic | Breaks down nutrients to release energy |
| Anabolic | Builds and stores energy and tissue |
When your metabolism is optimized, it runs efficiently—and fat burning is normal.
When it’s slowed:
- Fat accumulates
- Energy tanks
- Cravings intensify
⚙️ Why Low Energy Slows Metabolism
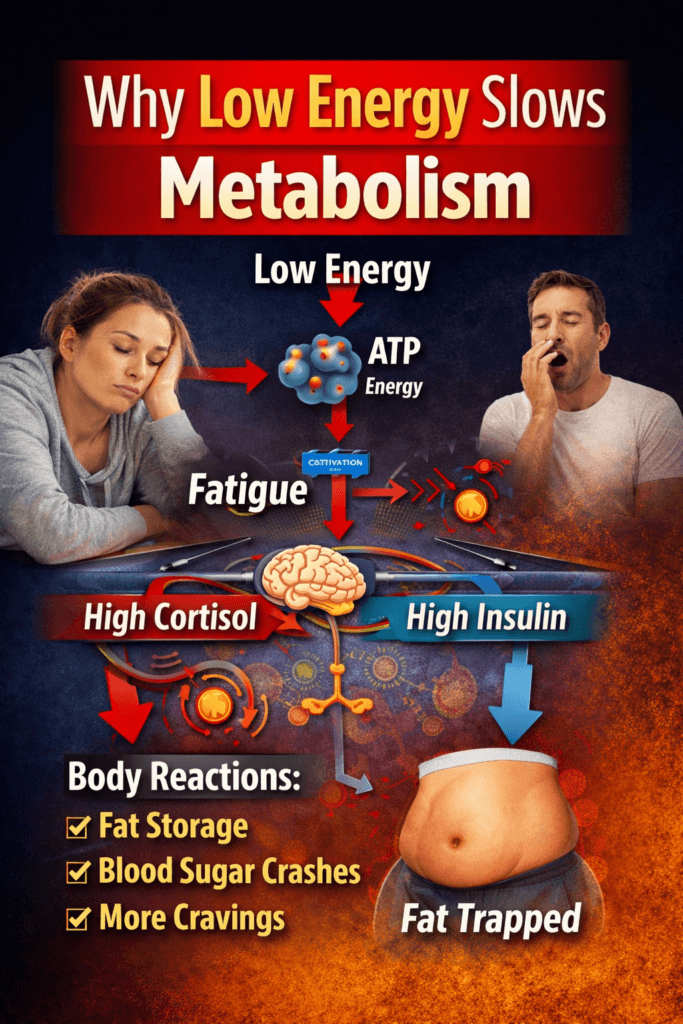
Your metabolism depends on your body’s ability to:
- Convert food (especially glucose) into usable energy
- Signal cells to burn energy instead of storing it
When energy production is impaired, your body activates survival pathways designed to conserve fuel—not burn fat.
The key drivers of slowed metabolism
✔ Low energy signals
✔ High cortisol
✔ Insulin resistance
✔ Poor sleep
✔ Frequent blood sugar spikes/crashes
These factors keep your body in storage mode instead of burn mode.
🔁 Energy Production 101
When you eat:
- Carbohydrates → glucose in blood
- Insulin moves glucose into cells
- Cells produce ATP—usable energy
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the unit of usable energy.
If ATP production is inefficient:
- You feel tired
- Your metabolism slows
- Fat burning stops
👉 Why Your Body Stores Fat When You’re Tired—energy + hormones
👉 How Blood Sugar Spikes Lock Belly Fat in Place—Insulin and metabolism
📊 How Low Energy Shifts Your Body into Fat Storage
Here’s how the biology works:
| Signal | Body Reaction |
|---|---|
| Low ATP (energy) | Increase cortisol to mobilize fuel |
| High cortisol | Blocks fat burning & increases fat storage |
| High insulin | Stores glucose as fat |
| Frequent blood sugar swings | Trigger cravings & metabolic stress |
When these signals are repeated day after day:
🎯 Your fat cells become resistant to fat release
🎯 Your metabolism prefers storage
🎯 Belly fat accumulates
This is not about willpower—it’s about signal hierarchy.
🧬 The Science: Metabolism & Hormones
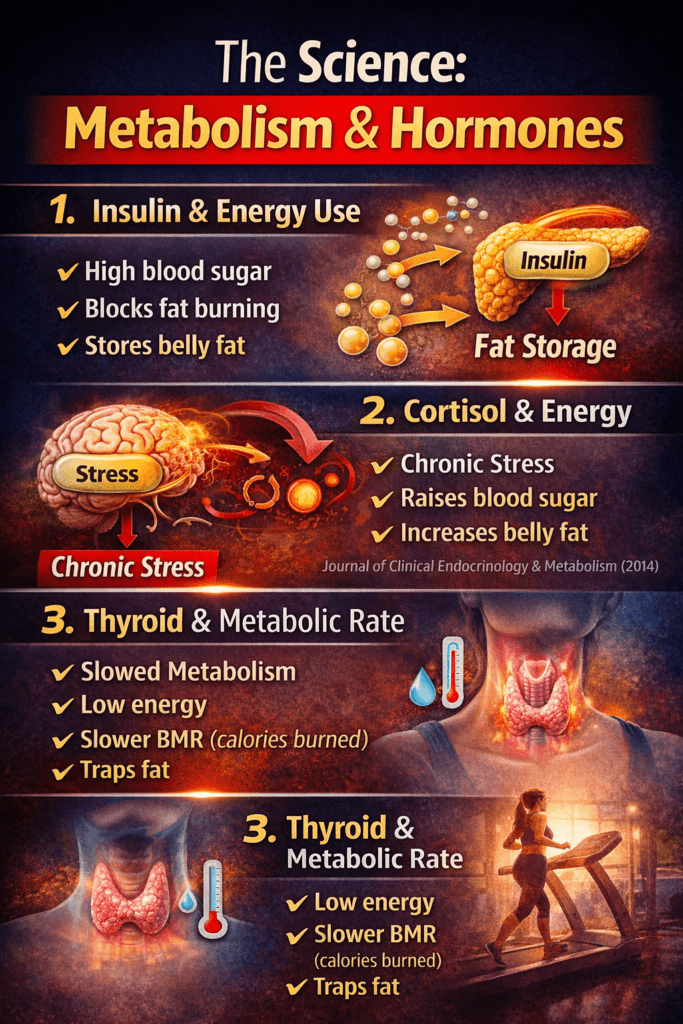
1. Insulin and Energy Use
Insulin helps glucose enter cells.
But chronically high blood sugar (from refined carbs, sugar, and low-protein meals) causes:
- Insulin resistance
- Cells that don’t use glucose effectively
- Higher stored fat
This is one reason belly fat is stubborn—visceral fat has more insulin receptors.
Source: Diabetes Journal (2014).
2. Cortisol and Energy
Cortisol rises when energy signals are low (like during stress or poor sleep).
Chronic cortisol increases:
- Appetite
- Blood sugar
- Fat storage around the belly
Source: Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2014).
3. Thyroid & Metabolic Rate
Your thyroid drives your basal metabolic rate (BMR).
Low energy, stress, and poor sleep can suppress thyroid signaling—reducing resting metabolism and fat burning.
🌟 How to Stabilize Your Energy & Restart Fat Burning

You don’t fix fat loss through calorie cutting—you fix the metabolic signals.
✅ 1) Prioritize Protein at Every Meal
Protein:
- Stabilizes blood sugar
- Stimulates muscle repair
- Supports lean metabolism
Study: Higher protein diets improve metabolic rate and satiety.
Source: American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2015)
✅ 2) Add Low-Impact Movement (Daily Walks)
Post-meal walking helps glucose go into muscles without insulin.
Source: Diabetes Care (2016)
✅ 3) Proper Sleep (7–8 Hours)
Even one night of poor sleep reduces insulin sensitivity and raises cortisol.
Source: The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2015)
🥤 4) Smoothies That Support Energy & Metabolism
One of the easiest metabolism resets is a balanced smoothie—with:
✔ Protein (Greek yogurt, whey, plant protein)
✔ Fiber (greens, chia seeds)
✔ Low-GI fruits (berries)
✔ Healthy fats (almond butter, avocado)
Even research supports balanced, protein-rich meals that blunt blood sugar swings and support energy production.
👉 Try the 21-Day Smoothie Challenge to Flatten Belly Fat and Boost Energy Naturally
📍 Quick Reference Table: Metabolic Reset
| Habit | Metabolic Impact |
|---|---|
| Protein | Stabilizes blood sugar |
| Walking | Improves glucose use |
| Sleep | Lowers cortisol |
| Balanced smoothies | Sustains energy |
| Stress control | Reduces metabolic block |
FAQ (Schema Ready)
Q1: Why does low energy slow my metabolism?
A: Low energy causes your body to shift into survival mode, raising cortisol and insulin, which favors fat storage over fat burning.
Q2: Can I fix metabolism without dieting?
A: Yes—stabilizing blood sugar and cortisol and improving sleep boosts your body’s energy use and fat burning.
Q3: Does more exercise always help?
A: Intense workouts without recovery can raise stress hormones. Focus on balanced movement (walking, strength training).
Q4: Will smoothies help my energy?
A: When made right (protein, fiber, healthy fats), smoothies can stabilize glucose and boost sustained energy.
Q5: How long before I see changes?
A: Many people notice improved energy in 1–2 weeks with consistent sleep and balanced meals; body composition changes follow with consistency.
🧠 Final Thought
Your metabolism is not broken—it’s reacting to signals: energy, stress, hormones, and food quality.
When you fix the signals,
Your body stops saving energy and starts burning fat again.
If you’re exhausted, have low energy, and have belly fat, then tell me below:
What’s your biggest energy struggle—sleep, cravings, or fatigue? 👇
